Unraveling Insulin Resistance(IR): Mechanism Exploration and Implications
1. Introduction to Insulin
Insulin is an amino acid polypeptide synthesized by pancreatic β-cells, with a molecular weight of 5802 Da, consisting of an α-chain (21 amino acids) and a β-chain (30 amino acids) connected by two disulfide bonds [1][2].

Insulin plays a crucial regulatory role in glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and protein metabolism. The following figure illustrates the systemic circulation process of insulin.

Figure.1 The systemic circulation process of insulin [3]
2. Insulin Resistance
Glucose metabolism is essential for maintaining energy homeostasis, with insulin as a key participant. When insulin binds to its receptor, it triggers a cascade involving proteins such as IRS, PI3K, AKT, leading to glycogen storage. Insulin resistance occurs when there is a reduction in insulin receptors, insufficient insulin binding, and impaired GLUT4-mediated glucose transport (see Figure 2 for the metabolic process).
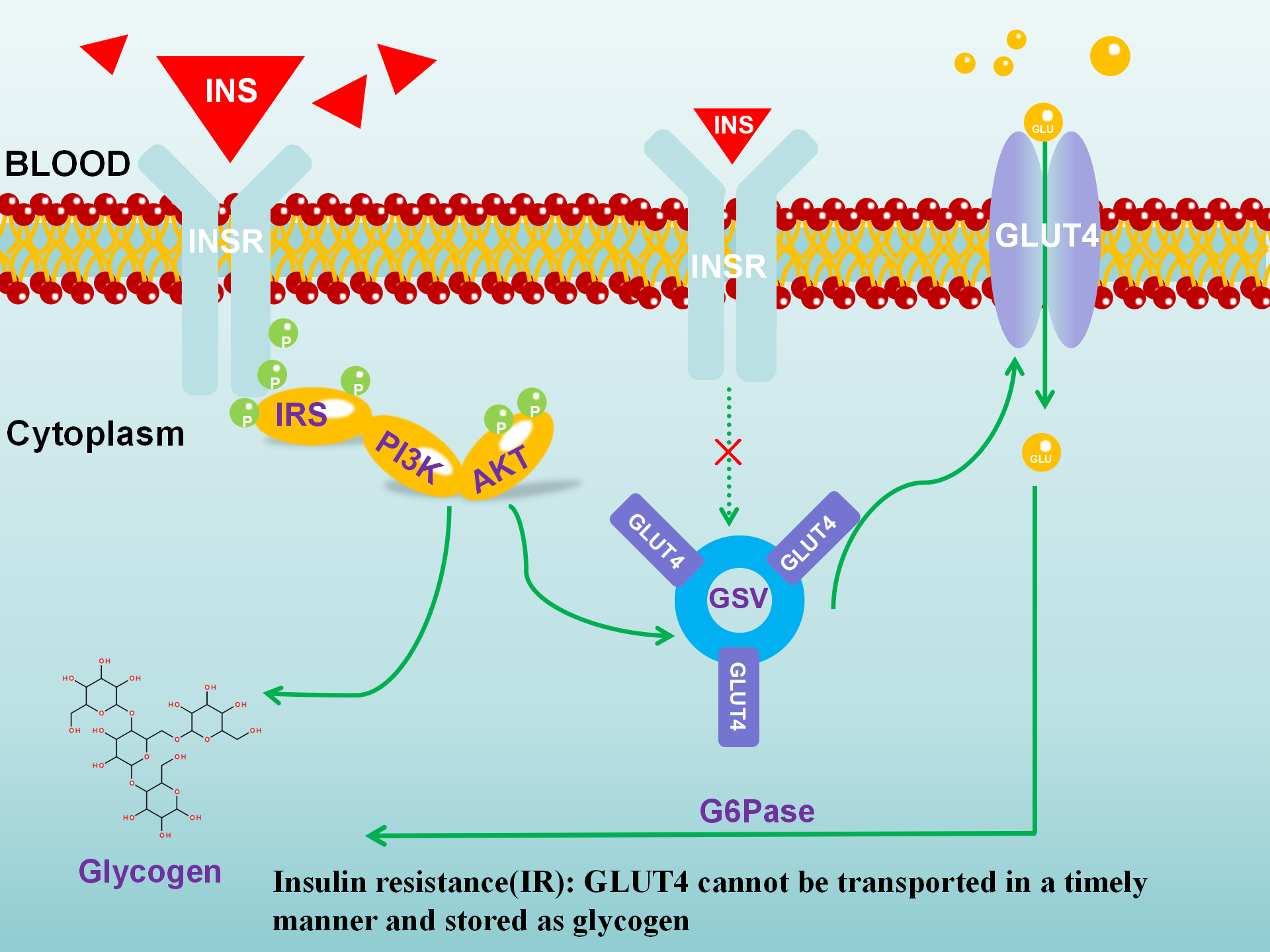
Figure.2 The metabolic process of insulin
(IR: Insulin Receptor Substrate,IR: Insulin Receptor,PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase,AKT: Serine/Threonine Kinase, GLUT4: Glucose Transporter Type 4,GSV: GLUT4 Storage Vesicle)
3. Evaluation Criteria for Insulin Resistance
The gold standard for assessing insulin resistance is the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp technique, which offers high accuracy and repeatability. However, its clinical application is limited by high costs and equipment requirements. The Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) is widely favored due to its simplicity and effectiveness in reflecting insulin resistance. The core formula is:
HOMA-IR=FI(μIU/mL)*FPG(mmol/L)/22.5
where FI is fasting plasma insulin concentration and FPG is fasting blood glucose. Researchers can calculate HOMA-IR using these parameters. Reference values for HOMA-IR are shown in Table 1, noting that thresholds may vary by ethnicity, age, and laboratory (e.g., lower values in Asian populations).
Table .1 Reference values of HOMA-IR for human
|
Poeple |
Reference Range |
Clinical significance |
|
Healthy people |
<1.0 |
Normal insulin sensitivity |
|
Critical insulin resistance |
1.0-1.8 |
Be alert to the risk of metabolic syndrome |
|
Clarify insulin resistance |
≥1.9 |
Revealing Insulin Resistance |
|
Significant insulin resistance |
≥22.5 |
High risk of diabetes/cardiovascular disease |
Note:The threshold values may vary slightly among different races, ages, and laboratories (e.g. Asian populations may have lower thresholds) .The reference values for children and adolescents need to be adjusted according to age.
4.Conversion Between Insulin Concentration and Activity Units
For researchers measuring insulin levels, unit conversion between mass (e.g., mg) and activity (e.g., IU) is essential. According to the WHO (https://nibsc.org), human insulin specifications are:


Figure.3 WHO Website Information on Insulin
According to WHO documentation: 1mIU/L=1μIU/mL=34.7pg/mL.Given the relative molecular mass of insulin (5802), then 1 mIU/L = 34.7/5.802 ≈6 pmol/L
5.Does Reed Biotech Offer Related Products?
Reed Biotech provides the following insulin-related ELISA kits:
|
Catalog No. |
Assay Target |
Species |
|
RE3153H |
Human |
|
|
RE3153M |
Mouse |
|
|
RE3153R |
Rat |
Reference
